User Psychology in Game Design: How to Build Player-Centric Experiences
Great game design isn’t just about mechanics or visuals — it’s about understanding how players think, feel, and behave.
At its core, game design is the design of human behavior through systems. Every mechanic, interface decision, and progression loop subtly teaches players how to act, what to value, and why they should keep going. When designers understand the psychological forces at play, they can build experiences that feel intuitive, engaging, and meaningful rather than manipulative or exhausting.
This article explores key psychological principles that shape player-centric game design and how they influence engagement, immersion, and long-term satisfaction.
Motivation: Why Players Engage
One of the most widely referenced frameworks in game psychology is Self-Determination Theory, which identifies three core drivers of intrinsic motivation:
Autonomy — the feeling of choice and control
Competence — the sense of growth and mastery
Relatedness — connection to others or to the world itself
Games that respect player autonomy allow meaningful decisions rather than forcing rigid paths. Competence is built through clear feedback and fair challenges that reward learning. Relatedness can emerge through narrative, shared spaces, or social mechanics that encourage cooperation rather than exploitation.
When these elements align, engagement feels natural. When they’re missing, players disengage — or worse, feel coerced into continuing.
Cognitive Load & Information Processing
Before players can enjoy a system, they must understand it.
Cognitive load refers to the amount of mental effort required to process information. Overly complex interfaces, unclear feedback, or too many simultaneous mechanics overwhelm players and break immersion. Well-designed games manage cognitive load by:
Introducing systems gradually
Using clear visual hierarchies
Reinforcing learning through consistent feedback
Once players understand the rules of a system, they can focus on strategy, expression, and mastery instead of deciphering the interface.
Clarity isn’t simplification — it’s respect for the player’s attention.
Reward Systems & Player Motivation
Once players understand a game, the next question becomes how that system reinforces continued engagement.
Reward systems — XP, loot, achievements, progression — shape player behavior more than any single mechanic. When designed well, they reinforce learning and effort. When designed poorly, they create dependency rather than satisfaction.
Poorly tuned reward systems can subtly shift player behavior away from play and toward optimization, where efficiency replaces enjoyment. This mirrors broader concerns explored in When Tools Begin to Decide, where systems begin making decisions on behalf of users rather than supporting judgment.
The goal isn’t constant stimulation. It’s earned progression that reinforces trust.
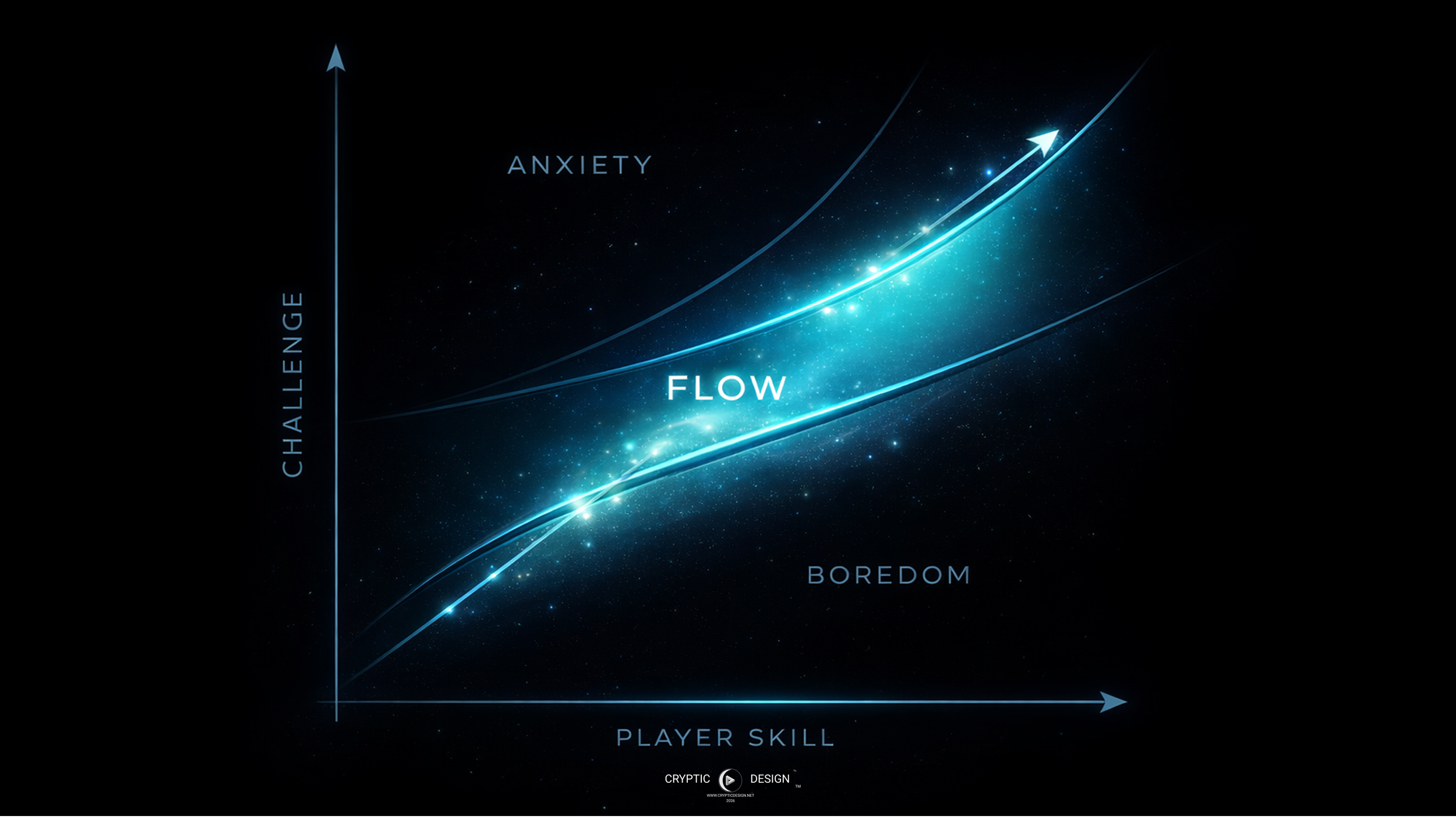
Flow State & Immersion in Game Design
The concept of flow, introduced by Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, describes a mental state where challenge and skill are perfectly balanced. In games, flow emerges when:
Tasks are neither trivial nor overwhelming
Feedback is immediate and clear
Progress feels earned, not random
When players enter flow, time disappears. Friction fades. Engagement becomes intrinsic rather than forced.
A practical example of how flow can succeed — and where it can fray — can be seen in ARC Raiders: A Player Experience Review, where strong moment-to-moment immersion competes with long-term systemic pressure.
Emotional Design: Evoking Player Connection
Beyond mechanics and progression, emotion is what players remember.
Atmosphere, narrative framing, sound design, and visual tone all contribute to emotional resonance. Emotional design isn’t about cinematic excess; it’s about aligning the player’s internal state with the experience the game wants to deliver.
When emotion supports mechanics, players feel invested. When it conflicts, immersion collapses. Emotional design bridges the gap between systems and meaning, giving context to player actions rather than leaving them hollow.
Conclusion: Designing With Responsibility
Understanding player psychology isn’t about control — it’s about responsibility.
Games are systems that shape behavior, attention, and motivation. Designers decide whether those systems empower players or quietly exploit them. Player-centric design respects autonomy, supports learning, and values trust over retention metrics.
This perspective extends beyond games into everything we build at Cryptic Design, reflected in our broader approach to designing human-centered systems.
Because the systems we create don’t just entertain — they teach people how to think, act, and engage with the world.
Continue the Conversation
Thoughtful design invites thoughtful discussion.
If this article sparked an idea or a disagreement, continue the conversation here:
LinkedIn · X · Facebook